Future path
The Golden Future and Talent Opportunities in Taiwan's Semiconductor Industry
The semiconductor industry is the lifeline of Taiwan's economic development and represents technological innovation and high-paying careers.
According to report estimates, the talent gap in Taiwan's semiconductor industry will reach 34,000 people by May 2025. The three main job categories in demand are:
- - Production/Manufacturing & Quality Control (approx. 10,000 people)
- - R&D (approx. 9,000 people)
- - Operation/Technical/Maintenance (approx. 7,000 people)
The overall average industry salary is generally 20% to 30% higher than other manufacturing sectors. Engineers with specialized skills, especially in R&D and process-related positions, have the opportunity for an annual salary exceeding one million NTD.
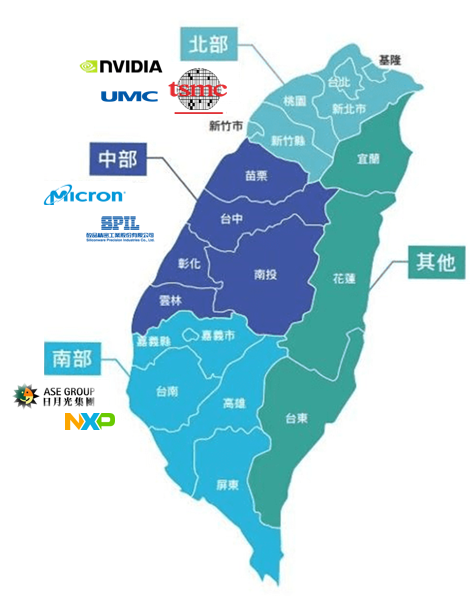
Taiwan's industry clusters are highly concentrated in the Northern, Central, and Southern Science Parks, forming a complete supply chain:
- ▶️ North: Hsinchu (HSP) – Wafer Fab/IC Design (e.g., TSMC)
- ▶️ Central: CTSP – Packaging & Testing/Memory (e.g., Micron)
- ▶️ South: STSP – Packaging & Testing/Automotive Chips (e.g., ASE Group)
Main Industry Distribution and Companies (See Map)
[Program Introduction] Industry Core & Learning Tracks
The semiconductor industry covers fields such as IC Design & Device Simulation, Wafer Fabrication, Advanced Packaging & Testing, Materials & Equipment, and Smart Manufacturing & Data Application.
This program structures its courses and practical training around four main tracks: "IC Design & Device Simulation", "Process & Equipment", "Packaging & Measurement", and "Smart Manufacturing & Cyber-Physical Integration". Through industry mentors, industry-academia projects, and internships, it helps students sequentially build employability and job-ready skills.
💪 The Five Core Competencies You Will Build (Core Competencies)
1. IC Design & Device Simulation
- Design chip architecture, simulate circuits, and implement layouts.
- Requires knowledge of hardware languages (e.g., Verilog) and EDA design tools.
2. Process & Integration
- Stabilize process parameters, troubleshoot issues, and analyze yield.
- Requires understanding of process principles, statistical analysis, and cross-departmental communication.
3. Equipment & Facilities
- Maintain machinery to improve uptime and ensure facility system safety.
- Requires skills in mechatronics, PLC automation, and safety management.
4. Packaging, Test & Failure Analysis
- Manage back-end packaging, electrical measurement, and failure cause analysis.
- Requires knowledge of packaging materials, measurement tools (SPC), and reliability.
5. Smart Manufacturing & Data Application
- Analyze manufacturing data, optimize systems, and predict equipment maintenance.
- Requires data analysis, programming fundamentals, and manufacturing systems knowledge.
Career Roadmap and Job Categories (Career Roadmap)
Explore the four core domains of the semiconductor industry and find the professional track that suits you best.

A. IC Design & Device Simulation
- Common Job Titles
- Digital/Analog IC Design Engineer, Chip Verification Engineer, Layout Engineer, Device Simulation & Model Development Engineer
- Key Responsibilities
- Chip architecture design, circuit simulation analysis, design verification & layout implementation, device characteristic simulation
- Required Skills
-
- Fundamentals of electronic circuits and semiconductor devices
- Verilog/VHDL Hardware Description Languages
- SPICE simulation and EDA design tool application
B. Process & Integration
- Common Job Titles
- Thin Film, Etch, Diffusion, Photolithography Process Engineer; Integration Engineer; Yield & Reliability Engineer
- Key Responsibilities
- Process parameter setting and stabilization, cross-site troubleshooting, yield and reliability analysis
- Required Skills
-
- Semiconductor process principles
- Statistical analysis and Design of Experiments (DOE)
- Cross-departmental communication
C. Equipment & Facilities (incl. EHS)
- Common Job Titles
- Equipment Engineer, Facilities Engineer (Gas, Vacuum, Cleanroom), EHS Engineer
- Key Responsibilities
- Machine maintenance and uptime improvement, preventive maintenance, system safety and regulatory compliance
- Required Skills
-
- Mechatronics
- Vacuum and utility systems
- PLC Automation
- Safety Management
D. Packaging, Test & Failure Analysis
- Common Job Titles
- Packaging Process & Materials Engineer, Electrical & Optical Test Engineer, Failure Analysis Engineer
- Key Responsibilities
- Packaging flow and materials, measurement and QA, thermal and mechanical design concepts, packaging structure and materials science, measurement tools and SPC, reliability methods
- Required Skills
-
- Packaging structure and materials science
- Measurement tools and SPC
- Reliability methods
E. Smart Manufacturing & Data Application
- Common Job Titles
- Manufacturing Data Analysis, Predictive Maintenance, MES & Cyber-Physical Integration
- Key Responsibilities
- Data processing, equipment health management, system integration and process optimization
- Required Skills
-
- Data Analysis
- Programming Fundamentals
- Manufacturing systems and information integration




